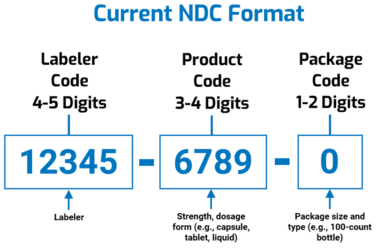
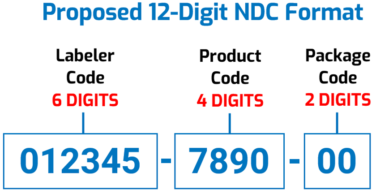
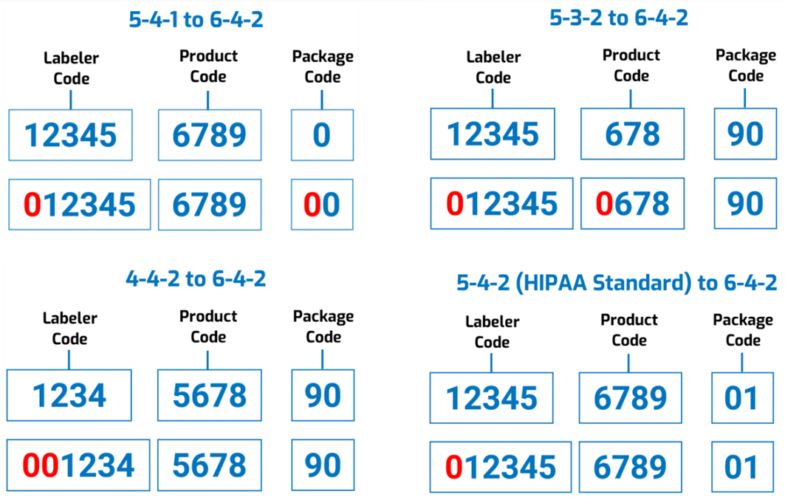
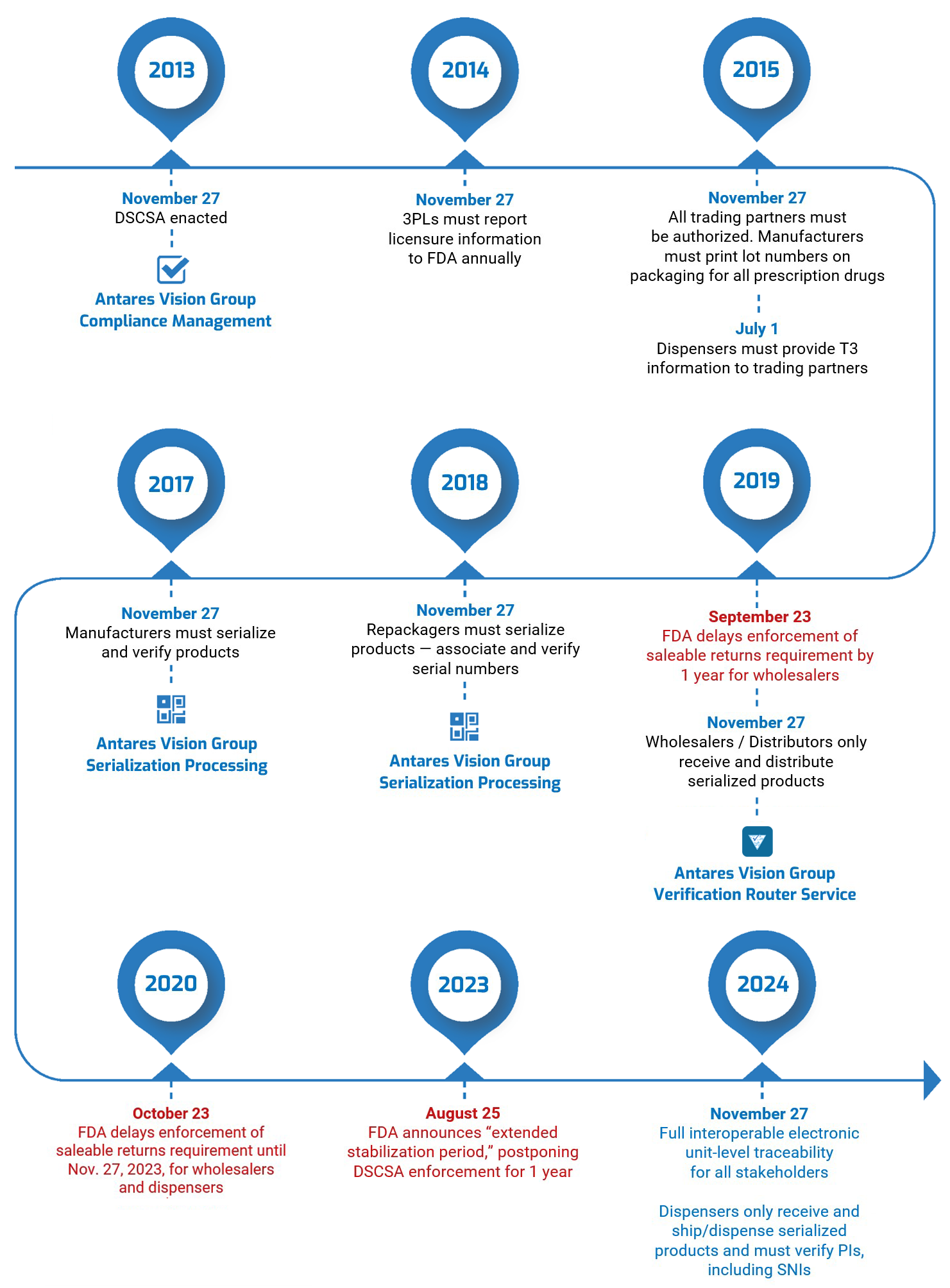
Antares Vision Group, through rfxcel technology, has integrated Spherity’s Credentialing Service into its DSCSA solutions to verify authorized trading partners’ identities and licensing in all regulated interactions.
Reno, Nevada, April 25, 2023 — Spherity, a German leading provider of digital wallet and credentialing solutions, and Antares Vision Group, an Italian multinational and a leading provider of track and trace and quality control systems, are continuing a partnership that helps ensure life sciences customers comply with this year’s U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) regulations.
By November 27, 2023, manufacturers, distributors, dispensers, and other actors in the life sciences supply chain must prove that they are legitimate organizations, or authorized trading partners (ATPs), as defined by the DSCSA.
The two companies first partnered in 2021, when Spherity’s Credentialing Solution, CARO, was integrated into the Group’s Verification Router Service (VRS) solution, enabled by rfxcel technologies, to allow life science customers to confirm their ATPs status. The combined solution also allows customers to exchange DSCSA-compliant electronic Product Identifier (PI) messages, trace products, and create an audit trail of their VRS business interactions.
CARO uses Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) technology to establish a secure, verifiable digital enterprise identity for every ATP. By integrating the service into its VRS solution, rfxcel customers can ensure secure, authenticated data exchange with other ATPs and verify they have the credentials required by the DSCSA, including state licenses and U.S. Food and Drug Administration Entity Identifiers (FEIs).
“We partnered with Spherity to enable our customers to comply with this year’s DSCSA authorized trading partner (ATP) requirements,” said rfxcel Senior Vice President of Product and Strategy Herb Wong. “With Spherity’s CARO, our VRS solution automatically confirms whether a company is an ATP. Now, every customer can add ATP credentialing to our entire product portfolio and secure their VRS interactions.”
“Spherity will ensure that Antares Vision Group’s customers can securely exchange data with previously unknown entities,” said Georg Jürgens, Spherity’s Manager for Industry Solutions. “The concept of exchanging and verifying credentials using Digital Wallets supports company and product compliance use cases that require communication between regulators, existing supply chain partners, and new trading partners.”
Spherity and Antares Vision Group are members of the Open Credentialing Initiative (OCI), and both contribute to the standardization and industry-wide interoperability of credentialing technology.
For more information about the Spherity-Antares Vision Group partnership, their solutions for DSCSA compliance with ATP requirements, and the Open Credentialing Initiative, contact Spherity’s Manager for Industry Solutions Georg Jürgens at georg.juergens@spherity.com and visit caro.vc, and rfxcel Senior Vice President of Product and Strategy Herb Wong at hwong@rfxcel.com.
ABOUT ANTARES VISION GROUP
Antares Vision Group is an outstanding technology partner in digitalization and innovation for companies and institutions, guaranteeing the safety of products and people, business competitiveness, and environmental protection. The Group provides a unique and comprehensive ecosystem of technologies to guarantee product quality (inspection systems and equipment) and end-to-end product traceability (from raw materials to production, from distribution to the consumer) through integrated data management, applying artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. Antares Vision Group is active in life science (pharmaceutical, biomedical devices and hospitals) and Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), including food, beverage, cosmetics, and glass and metal containers. As a world leader in track and trace solutions for pharmaceutical products, the Group provides major global manufacturers (over 50% of the top 20 multinationals) and numerous government authorities with solutions, monitoring their supply chains and validating product authenticity. Listed since April 2019 on the Italian Stock Exchange in the Alternative Investment Market (AIM) segment and from 14 May 2021 in the STAR segment of Euronext; furthermore, from July 2022 included in the Euronext Tech Leaders index, dedicated to leading tech companies with high growth potential. In 2022, Antares Vision Group recorded a turnover of €223.5 million. The Group operates in 60 countries, employs more than 1,100 people, and has a consolidated network of over 40 international partners. To learn more, please visit www.antaresvision.com and www.antaresvisiongroup.com.
ABOUT SPHERITY
Spherity is a German software provider bringing secure and decentralized identity management solutions to enterprises, machines, products, data and even algorithms. Spherity provides the enabling technology to digitalize and automate compliance processes in highly regulated technical sectors. Spherity’s products empower cybersecurity, efficiency and data interoperability among digital value chains. Spherity is certified according to the information security standard ISO 27001.