Drug Supply Chain Security Act pharmacy responsibilities are complex. They can be confusing. But the clock continues to count down to the final compliance deadline.
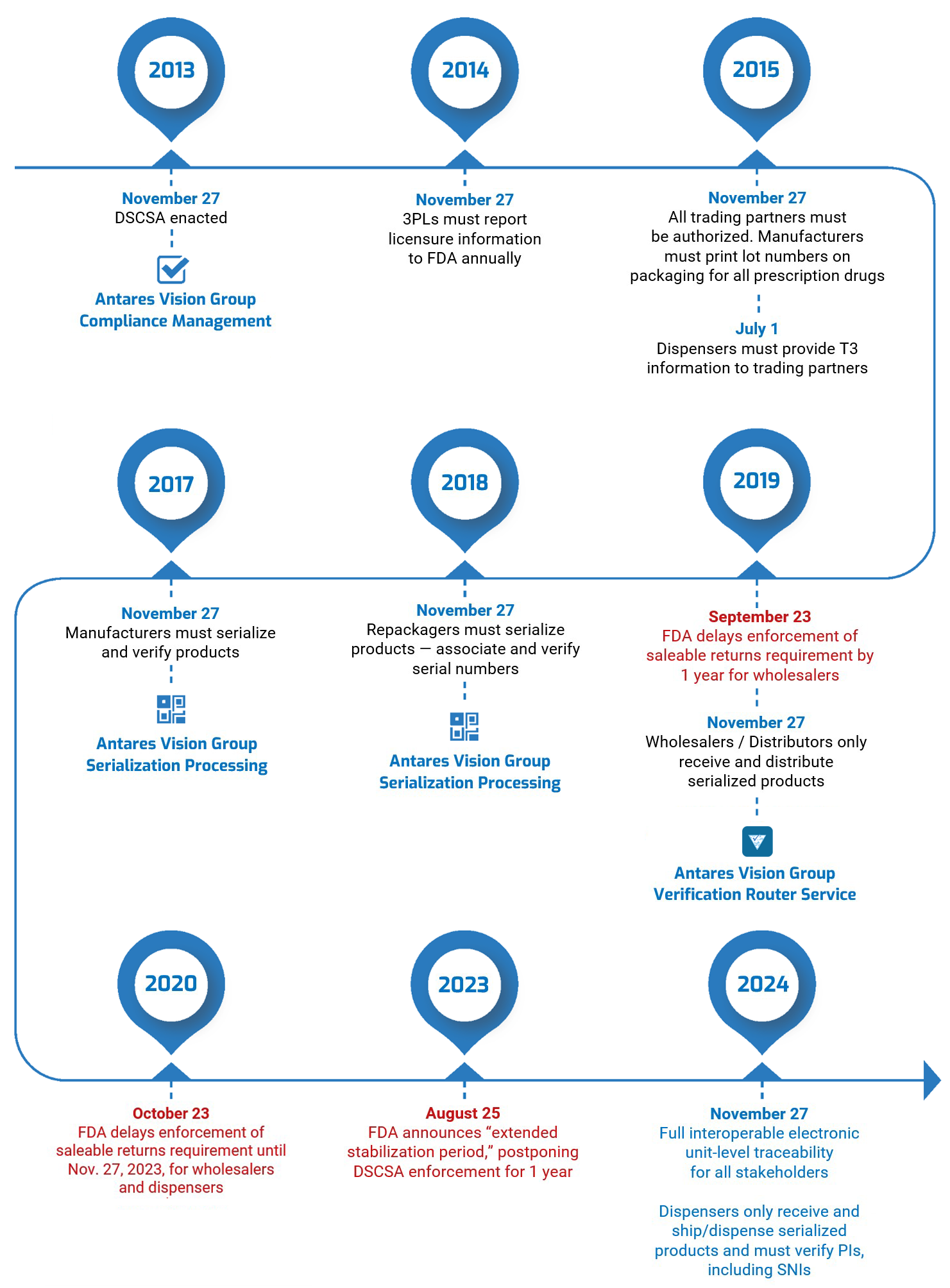
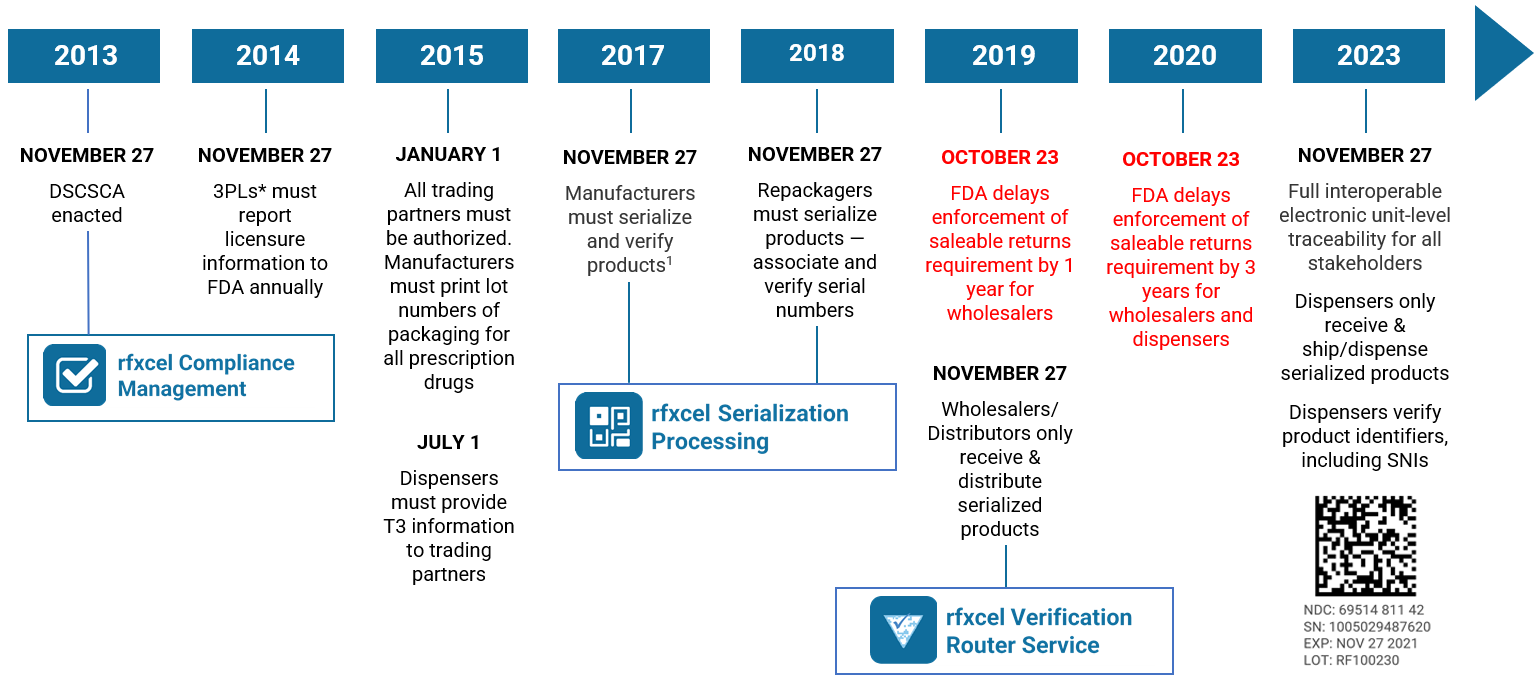
On August 25, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that it was delaying by one year enforcement of key DSCSA requirements. This “extended stabilization period” moves the enforcement date to November 27, 2024. Read our blog post here for all the details.
If you want to ensure that your business processes comply with DSCSA pharmacy regulations, the first step is to familiarize yourself with the nuances of the law. With that in mind, let’s do a quick recap for pharmacies.
What is the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act?
The U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act, enacted on November 27, 2013, establishes a system to track and trace prescription drugs in a fully serialized supply chain. It calls for end-to-end traceability and electronic interoperability to prevent counterfeit, stolen, contaminated, or otherwise harmful drugs from entering the U.S. supply chain.
So far, the DSCSA has mostly focused on lot-level traceability — exchanging information about every package of medication so stakeholders can see exactly where it has been. Enactment will culminate next year with complete unit-level serialization of the U.S. drug supply chain. This means stakeholders will have to electronically track products at the individual package level.
As the final link in the pharmaceutical supply chain, pharmacies are the last safeguard between suspect products and patients. They are responsible for gathering transaction information and reviewing supply chain data to verify the legitimacy of products (more on that below).
Drug Supply Chain Security Act pharmacy responsibilities: definitions
Pharmacies are referred to as “dispensers” in the DSCSA. The legislation defines a dispenser as “a retail pharmacy, hospital pharmacy, a group of chain pharmacies under common ownership and control that do not act as a wholesale distributor, or any other person authorized by law to dispense or administer prescription drugs, and the affiliated warehouses or distribution centers of such entities under common ownership and control that do not act as a wholesale distributor.”
If you dispense only products to be used in animals, you are not a dispenser under the DSCSA. The DSCSA pharmacy requirements apply only to dispensers that provide medication to patients or end-users. If your pharmacy is providing medications to another dispenser or another member of the pharmaceutical supply chain, it is acting as a distributor, which means other DSCSA requirements would apply.
How to comply with the DSCSA
Compliance is mandatory if you are a dispenser under DSCSA pharmacy requirements. Failure to comply will raise flags with the FDA and open your organization to penalties, including fines.
As we said above, the Drug Supply Chain Security Act pharmacy responsibilities are complex. Let’s break them down into easy-to-understand pieces.
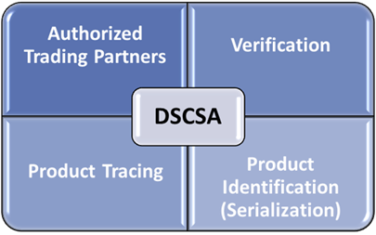
You must exchange information about every drug you buy and who handled it each time it changes ownership in the United States.
The DSCSA calls this “product tracing information,” and it has three components, collectively referred to as “T3 information”:
- Transaction Information (TI) about a product (e.g., proprietary or established name or names and the strength and dosage form)
- Transaction Statement (TS), which is an electronic statement confirming the entity transferring ownership.
- Transaction history (TH), an electronic statement with the TI for every transaction going back to the manufacturer. TH is required only until the November 27, 2024, deadline.
Under DSCSA pharmacy requirements, you have to obtain and exchange this data for every transaction. The purpose of these traceability requirements is to promote drug distribution security and to identify potential discrepancies in the supply chain records. If a product cannot be traced back to a legitimate source, it is considered “suspect.”
Adhering to these transaction requirements will help pharmacies protect their consumers from illegitimate drug products. Traceability standards also help the FDA ensure that suspect prescription drugs do not enter the supply chain in the first place.
You must receive, store, and provide product tracing documentation
You can accept prescription drugs only if they have proper tracing information, and you must store the information for six years. You must also generate and provide all information when you sell a prescription drug to a trading partner.
If the FDA conducts a DSCSA pharmacy audit, it can examine records dating back six years. If information is missing, you will be found in violation of the DSCSA and could face substantial penalties.
Providing product traceability information is another important part of DSCSA pharmacy requirements, as pharmacies frequently send inventory to other companies within their healthcare networks. When you engage in these activities, you are acting as a distributor and must adhere to all relevant standards regarding the creation of lot numbers and product-level tracing.
You can only do business with authorized trading partners (ATPs)
And speaking of trading partners, if you can’t confirm your they’re licensed or registered, you can’t do business with them. If they’re not authorized, their access to the U.S. pharma supply chain will be severely restricted or denied altogether. Read our in-depth ATP blog series for all the details.
For now, we will provide a brief recap of what constitutes an ATP under the DSCSA guidelines. The FDA states that an authorized partner is:
- A manufacturer or repackager that has a valid registration with the FDA
- A wholesale distributor that has a valid license under state law
- A third-party logistics provider (3PL) that has a valid license in accordance with state law
- A dispenser that has a valid license in accordance with state law
The FDA defines a trading partner as:
- An entity (i.e., manufacturer, distributor, repackager, or dispenser) that accepts director ownership of a product from a manufacturer
- An entity that transfers direct ownership of a product
- A 3PL that accepts or transfers products to another entity in the supply chain
In other words, an ATP is an entity that is appropriately licensed and accepts or transfers direct ownership of a regulated pharmaceutical product. Before a pharmacy does business with a repackager, wholesaler, or distributor, it must verify the organization’s ATP status.
You must investigate and properly handle suspect and illegitimate drugs
Suspect and illegitimate drugs include drugs that may be counterfeit, diverted, stolen, intentionally adulterated, or unfit for distribution — the problem the DSCSA was designed to eliminate. Pharmacies must quarantine and investigate these drugs to determine if they are fake. If you make this determination, the next step is to work with the manufacturer and take specific action to ensure the bad drug does not reach patients/consumers. You must also notify the FDA and your trading partners about the drug.
Identifying illegitimate products is one of the most important roles of pharmacists under DSCSA requirements. It is also one of the most challenging tasks, as each pharmacist and pharmacy technician must be trained on how to identify illegitimate or suspect products. All pharmacies should train their employees about the DSCSA requirements (e.g., abnormalities in transaction information) and other methods to identify suspect products.
You must authenticate and verify drugs
This is what’s coming in 2024. You’ll have to be able to authenticate and verify all the medicines you buy before you can sell them. The fundamental requirement is that TI (transaction information) must include a product identifier (PI), which includes serial numbers and expiration dates. The Electronic Product Code Information Services (EPCIS) is likely to be the standard the industry will use to enable this exchange.
EPCIS is a standard from GS1, an international organization responsible for creating and maintaining operational standards for key industries, including healthcare. EPCIS is a means to electronically share the “what, when, where, why, and how” information about pharmaceutical products, promoting end-to-end traceability and interoperability among supply chain actors.
Final thoughts
Navigating complex compliance requirements and adapting to new standards can present challenges. Fortunately, you have options — like partnering with rfxcel to help you meet DSCSA pharmacy requirements.
Even though the enforcement deadline has been extended until November 2024, the time to act is now. If you aren’t sure you’ll be ready, contact us to schedule a short demo of our DSCSA pharmacy compliance solutions, which include robust traceability tools, data management solutions, and more. As an rfxcel partner, you’ll tap into the expertise of our DSCSA pharmacy compliance experts, who will collaborate with you to design a solution to ensure you meet all DSCSA requirements and remain compliant forever.
We also invite you to download our DSCSA compliance white paper. It drills down into what we talked about today and is a great reference tool to have on hand as you prepare for the full serialization of the U.S. pharma supply chain. Also bookmark our DSCSA compliance library, which has all our resources about the law.