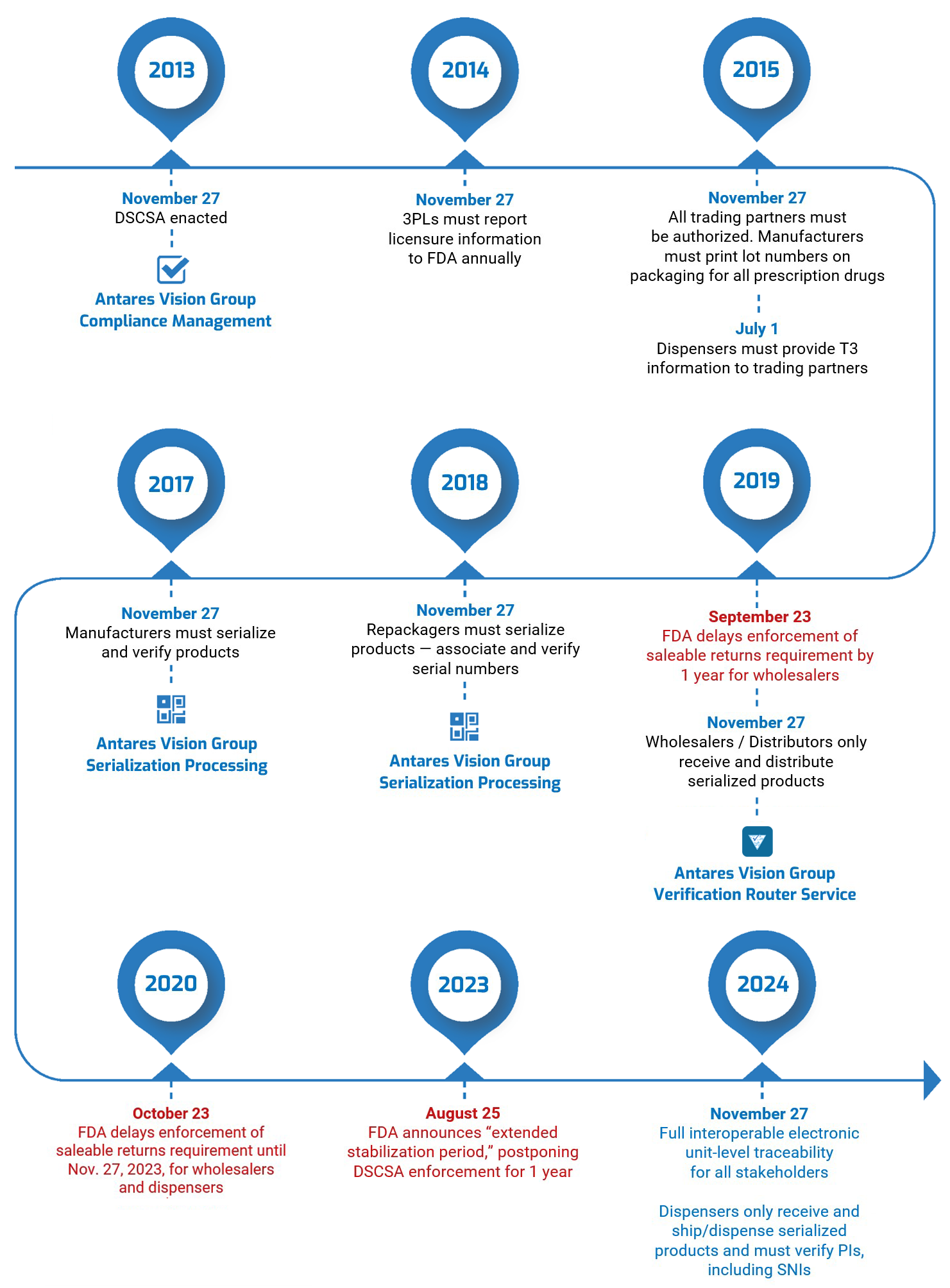
In a guidance document published on Friday, August 25, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that it was delaying by one year enforcement of key requirements under the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA). This “extended stabilization period” moves the enforcement date to November 27, 2024.
The guidance is primarily for manufacturers, wholesale distributors, dispensers, and repackagers; delayed enforcement pertains to product identifiers at the package level; saleable returns; interoperable, electronic product tracing; and investigating suspect and illegitimate products. We provide the specifics below.
The key takeaway: Don’t stop preparing for the DSCSA requirements. If you have questions about the DSCSA delay or are concerned that your current provider may not have the tools you need to comply, we encourage you to contact us today to speak with one of our DSCSA experts. We are committed to meeting DSCSA compliance for all our customers in a timely manner.
And if you’re going to the Healthcare Distribution Alliance (HDA) 2023 Traceability Seminar in Washington, D.C., stop by Table-Top 21 to meet our team and talk about the developments in person. Click here to learn more.
Overall FDA rationale for the DSCSA delay
The FDA said extending enforcement will give supply chain stakeholders — particularly manufacturers, wholesale distributors, dispensers, and repackagers — the extra time that may be necessary “to continue to develop and refine appropriate systems and processes to conduct interoperable, electronic tracing at the package level, to achieve robust supply chain security under the DSCSA while helping ensure continued patient access to prescription drugs.”
Furthermore, the Agency said, “additional time beyond November 27, 2023, may be needed for systems to stabilize and be fully interoperable for accurate, secure, and timely electronic data exchange.”
What DSCSA requirements are affected?
Product identifiers
The requirement. Trading partners must include the product identifier at the package level for each package in a transaction into the transaction information. Furthermore, a product’s manufacturer or repackager must incorporate the PI at the package level for each package “introduced in a transaction into commerce.” These requirements are included in section 582(g)(1)(B) of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetics Act (FD&C Act).
Reasoning for DSCSA delay. The FDA said the delay will “accommodate the additional time (beyond November 27, 2023) that may be needed by trading partners to achieve compliance and to help ensure continued access to prescription drugs as trading partners continue to refine processes” to include the PI at the package level. Furthermore, the FDA said “this policy will facilitate the use and exhaustion of product supply already in the supply chain prior to November 27, 2024.”
What is a PI? The PI is a standardized graphic that contains, in both human-readable form and on a machine-readable data carrier, four data elements:
-
-
- National Drug Code (NDC)
- Serial number
- Lot number
- Expiration date
-
Saleable returns
The requirement. Each person accepting a saleable return must have systems and processes in place to allow acceptance of the product. Furthermore, they may accept saleable returns only if they can associate the product with its transaction information — including the PI — and transaction statement. These requirements are included in section 582(g)(1)(F) of the FD&C Act.
Reasoning for DSCSA delay. FDA said delaying enforcement of this requirement until November 27, 2024, will “facilitate the continued use of methods currently being used by wholesale distributors for associating a saleable return product with its applicable transaction information and transaction statement while accommodating the additional time that may be needed for all trading partners to mature the new systems and processes required for acceptance of saleable returns.”
Interoperable, electronic product tracing at the package level
The requirement. Transaction information and transaction statements must be exchanged in a secure, interoperable, electronic manner. This requirement is included in section 582(g)(1)(C) of the FD&C Act; the standards for exchange are established under section 582(h) of the DSCSA.
Furthermore, systems and processes for verifying products at the package level, including the standardized numerical identifier, must meet the standards established in DSCSA section 582(a)(2) and the guidance in DSCSA section 582(h).
Reasoning for DSCSA delay. The FDA these policies will allow trading partners to continue to provide, capture, and maintain data for the data exchange for product tracing and verification while providing additional time that may be needed to “continue to develop and refine systems and processes for electronic data exchange.”
Investigating suspect and illegitimate products
The requirement. In the even of a recall or to help investigate a suspect or illegitimate product, stakeholders must be able to promptly provide product transaction information and transaction statement when requested by the FDA secretary or other appropriate federal or state official. This requirement is included in section 582(g)(1)(D) of the FD&C Act.
Furthermore, Section 582(g)(1)(E) of the FD&C Act requires stakeholders to “produce the transaction information for each transaction going back to the manufacturer” in certain situations, including a recall or investigating a suspect product or an illegitimate product.
Reasoning for DSCSA delay. FDA believes these compliance policies will facilitate the continued use of methods currently being used by trading partners to respond to the type of requests for information described above while accommodating the additional time that may be needed for trading partners to mature the new systems and processes required for such activities under section 582(g)(1)(D) and (E) of the FD&C Act.