It’s going to be a busy couple of years for the food industry as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) formalizes key parts of its plan to modernize and further secure the U.S. food supply chain. The next milestone for FDA food traceability regulations is just four months away, so let’s take a look at the requirements — and why food companies should embrace them as an opportunity to improve their businesses.
But first, if you’re intrigued by the idea that opportunities are “hiding” in the FDA food traceability regulations, join us for our “Safety, Regulatory Compliance & Beyond: Leveraging Traceability to Optimize the Food & Beverage Supply Chain” webinar on Wednesday, August 10, at 1 p.m. EST. Our experts will break down the “whys” and “hows” of traceability, discuss the real-world applications and value-adds, and take your questions.
Recap of FDA food traceability regulations & upcoming deadlines
Here’s a quick rundown of what’s on the table and upcoming deadlines.
Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA)
- Signed into law on Jan. 4, 2011
- Aims to ensure the food supply is safe by shifting the focus to preventing contamination rather than responding to it
- Applies to human food as well as to food for animals, including pets
- Establishes additional traceability recordkeeping requirements for people who manufacture, process, pack, or hold foods on the Food Traceability List
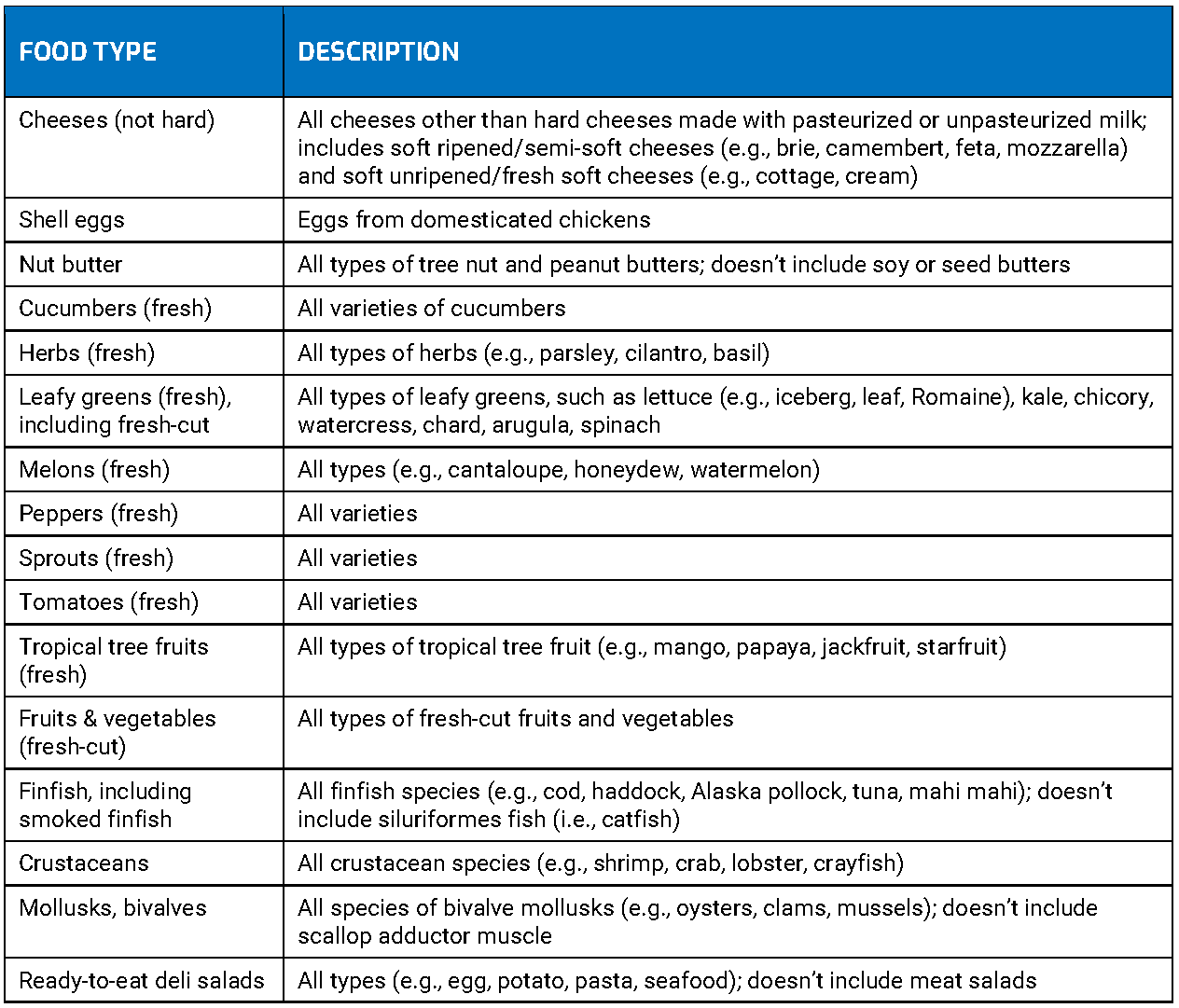
- Food Traceability List contains foods with additional traceability recordkeeping requirements (see table below)
- Stakeholders to establish and maintain records with key data elements (KDEs) associated with different critical tracking events (CTEs)
Key dates
- Nov. 7, 2022: FDA to finalize and submit the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Proposed Rule to the Federal Register
- January 2023: Proposed Rule goes into effect
- Jan. 6, 2025: Deadline for full compliance
The FDA has also launched the New Era of Smarter Food Safety and an accompanying New Era of Smarter Food Safety Blueprint, which envision a modern approach to ensuring food safety through digital, tech-enabled traceability. Get more details in our blog here.
FDA food traceability regulations: What to know now and how to seize opportunities
This is really just a preview of our August 10 webinar about leveraging traceability. We’ll touch on a few key points below; sign up for the webinar to take a deep dive.
Just the facts
The FSMA 204 deadlines are set. You’ll have to be fully compliant in about two years, so the time to prepare is now.
The Food Traceability List is a living document. More and more food items are sure to be added over time.
The FDA is committed to modernizing and securing the U.S. food supply chain. Expect the Agency to continue promoting (and regulating) traceability in a digital supply chain. This includes improving recall management.
Where’s the opportunity?
End-to-end traceability makes everything better. With the right solution, you’ll not only be compliant — you’ll make your supply chain faster, leaner, and more cost-effective.
“1-up, 1-down” is useful, but antiquated. Today, 1-up, 1-down traceability is merely a facet of end-to-end traceability (and visibility and transparency) in a digital supply chain. The right solutions transform your supply chain into an ecosystem that optimizes operations and creates opportunity and value beyond the point of sale.
Serialization is the building block of compliance — and added value. Serialization turns every product into a “digital asset” that can be traced in real time from virtually any location, yielding practical benefits to your operations. But these digital assets can accomplish much, much more, including brand protection and consumer engagement.
Traceability enables precise, targeted recall management — which means better outcomes for your brand. We’ve all heard the statistic that the average food recall costs $10 million. With traceability, you can locate specific items quickly, identify where they came from (e.g., grower, warehouse), take clear, decisive action to remove only those items from circulation, and protect consumers and your reputation.
Traceability in a digital supply chain means less clutter — literally. Do you have nightmares about back rooms full of boxes stuffed with paperwork? Traceability turns your nightmare into an operational dream. Get rid of all the paper and gain the power to quickly dial up any document, any time, from any location, including from mobile devices.
Traceability and added value
Traceability is the key to keeping consumers happy and inspired. Consumers are thinking deeply about the things they buy — where they come from and what goes into making them. They also expect to interact with the brands they trust. We wrote way back in October 2020 that supply chain traceability was building a new kind of consumer kingdom; it was true then, it’s true today, and it will be true tomorrow.
The era of digital assets and smart products is here. Products are no longer just products. With serialization and traceability, products are gateways to experiences. They’re beacons to broadcast information. They are conduits for hyper-targeted and hyper-personalized consumer engagement.
Final thoughts
FDA food traceability regulations are center stage in FSMA, the Food Traceability Proposed Rule (FSMA 204), the Food Traceability List, and the New Era of Smarter Food Safety. The deadlines are coming and you should be preparing.
But now you know that savvy companies will see traceability as more than a compliance mandate from the government — they’ll see it as a technology that creates a universe of opportunities for their businesses and brands.
Companies that are thinking only about the mechanics of complying with FDA food traceability regulations will miss these opportunities to be proactive about ensuring food safety and quality, reducing risks, protecting and building their brands, and leveraging every single product to connect with individual consumers in exciting, meaningful ways.
We don’t want you to miss these opportunities. To get started, sign up for our food traceability webinar to see how traceability works and how it delivers value.
Next, contact us to schedule a short demo of our food and beverage solutions, including our award-winning Traceability System and Mobile Traceability App. In about 15 minutes, our supply chain experts will show you how we create end-to-end traceability in a fully interoperable digital supply chain that’s visible anytime, anywhere.
Last, take a look at our other food traceability materials, some FDA links, and our shortened version of the Food Traceability List.
Our FSMA & Food Traceability Resources
- White Paper: Traceability in the Food Supply Chain
- FSMA Traceability: What the Food Industry Needs to Know Today
- FSMA Traceability Requirements: FDA Guidance & GS1 Standards
- FSMA 204 Data Carrier: FDA Guidance and GS1 Standards
- What is the FSMA Traceability Lot Code and Who Must Comply?
- Food Traceability Regulations in the United States: A Timeline
- Food Traceability: What’s the Latest for 2021?
- Food Traceability Gets Precise: The State of the Art
- Food Traceability Data: Not Just for Compliance Anymore
- Food Recall Management: Modernizing for a “New Era” of Food Safety
- Dairy Traceability in 2021: The FDA, the Industry, and the Future
- Meat Traceability in the Food Supply Chain: Getting to Know Your Protein
Other FDA Resources
- Food Safety Modernization Act
- Proposed Rule (FSMA 204)
- FSMA compliance dates
- FSMA reports & studies
- Frequently asked questions on FSMA
Food Traceability List