Note: This article was originally published in November 2021. We’ve since updated some language after the FDA announced on August 25, 2023, that it was delaying by one year enforcement of key DSCSA requirements.
November 27, 2023 — the date the pharmaceutical industry has had its sights on since the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) was enacted eight years ago. With only two years until the deadline, we thought it was a good time to recap what’s in store for DSCSA serialization.
What is DSCSA serialization?
DSCSA serialization is not different from serialization any other industry: It means that certain drugs must traceable at the unit level. Specifically, manufacturers and repackagers must put a unique Product Identifier (PI), such as a bar code, on certain prescription drug packages. This must be able to be read electronically. Furthermore, manufacturers, wholesale distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) must provide certain information about drug and who handled it each time it’s sold:
- Transaction information (TI) includes the product name; its strength and dosage form; its National Drug Code (NDC); container size and number of containers; lot number; transaction date; shipment date; and the name and address of the businesses from which and to which ownership is being transferred.
- The transaction statement (TS) is a paper or electronic attestation by the business transfer-ring ownership of the product that it has com-plied with the DSCSA.
- A third type of information, Transaction history (TH), is an electronic statement with the TI for every transaction going back to the manufacturer. It is not required after the law goes into effect on November 27, 2023; however, as we wrote about before, there is a “stabilization period” in effect until November 27, 2024, during which the FDA does not intend to take enforcement action. Read more about that here and below.
Meeting DSCSA serialization requirements is vital for all pharmaceutical supply chain members. Whether you are a manufacturer, wholesale distributor, or dispenser, DSCSA 2023 requirements apply to your business. The question is, are you ready?
The DSCSA 2023 deadline
As we just said, the DSCSA 2023 compliance deadline is still November 27. But the FDA postponed enforcement by one year to November 27, 2024. This change does not affect past deadlines on the DSCSA enforcement timeline, but does have implications for DSCSA requirements, including serialization.
This means that pharma stakeholders — manufacturers, wholesale distributors, repackagers, dispensers, and third-party logistics providers (3PLs) — now have an extra 12 months to get their systems in order. However, the FDA has made it clear that these entities should not regard the “stabilization period” as a delay of the 2023 requirements: It expects companies to have implemented the mandated systems and work to ensure they are operating correctly, smoothly, etc. The Agency’s Enhanced Drug Distribution Security Requirements Under Section 582(g)(1) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act — Compliance Policies states:
This guidance is not intended to provide, and should not be viewed as providing, a justification for delaying efforts by trading partners to implement the enhanced drug distribution security requirements under section 582(g)(1) of the FD&C Act. FDA strongly urges trading partners to continue their efforts to implement necessary measures to satisfy these enhanced drug distribution security requirements.
The DSCSA timeline
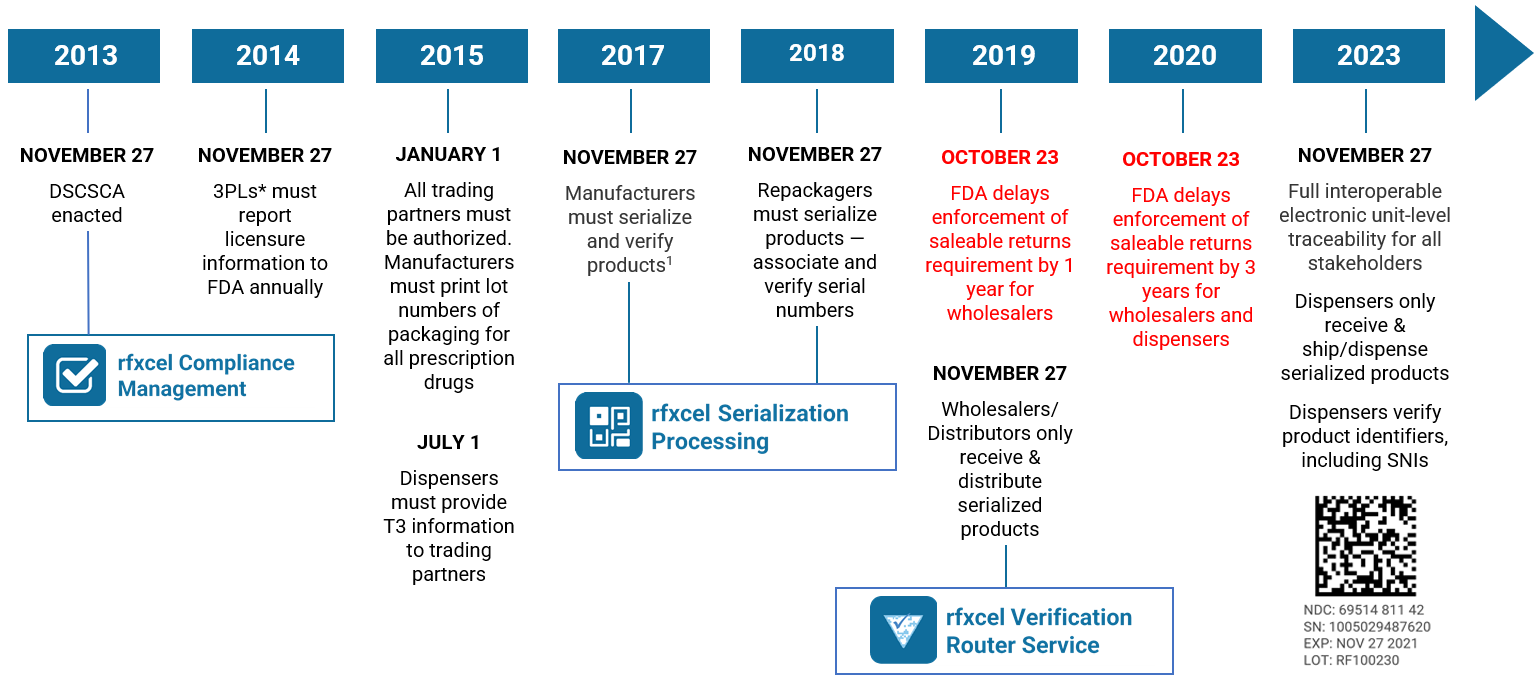
November 27, 2023, will be the 10th anniversary of the DSCSA. Per Section 582(g)(1) of the DSCSA (Title II of the Drug Quality and Security Act), “On the date that is 10 years after the date of enactment of the Drug Supply Chain Security Act … interoperable, electronic tracing of product at the package level requirements shall go into effect.” In other words, DSCSA 2023 serialization.
DSCSA serialization: recent developments
No more delays. On August 9, 2021, the FDA signaled that the DSCSA 2023 deadline for interoperability would not change. Leigh Verbois, the director of the FDA’s Office of Drug Security, Integrity, and Response, made the comments during a webinar hosted by the Healthcare Distribution Alliance (HDA).
Draft and final guidance on product identifiers (PIs) and more. On June 3, 2021, the FDA published “new guidance to further enhance the security of prescription drugs in the U.S. supply chain.” Guidance was released for PIs, suspect and illegitimate products, and enhanced drug distribution security.
Full serialization
For DSCSA serialization, certain drug packages must be labeled with a unique Product Identifier (PI). The PI comprises the National Drug Code, a serial number, a lot number, and an expiration date.
Furthermore, every time a product changes hands (i.e., between trading partners), supply chain actors must use the Electronic Product Code Information Services (EPCIS) to share Transaction Information (TI) and a Transaction Statement (TS) with their partners. A third requirement, Transaction History (TH), will not be required after the November 2023 deadline.
Even with the stabilization period until November 27, 2024, there’s no stopping the fact that significant changes are coming for pharmaceutical traceability under DSCSA. The primary focus? Serialization. Serialization involves assigning unique identifiers to each pharmaceutical product, enabling precise tracking and data reporting at every stage of its journey through the supply chain.
Authorized trading partners
Under the DSCSA, authorized trading partners (ATPs) may engage in transactions only with other ATPs. In other words, all manufacturers, wholesale distributors, repackagers, 3PLs, and dispensers and their trading partners must be ATPs. If they’re not authorized, their access to the U.S. pharma supply chain will be severely restricted or denied altogether. Read our in-depth ATP blog series here.
Verification Router Service (VRS)
Under the DSCSA saleable returns verification requirement, wholesalers must verify saleable returns before they can be reintroduced to the supply chain. This is done by verifying the drug’s PI. A wholesaler must initiate a verification request (to a manufacturer) to verify the returned products, and the manufacturer must provide a verification response within 24 hours. The VRS enables the rapid, secure exchange of data between these parties. Get more details here.
Final thoughts: DSCSA Serialization
We have been talking about and reporting on the DSCSA Day 1. We’ve been active in industry initiatives, particularly the VRS and the Open Credentialing Initiative (OCI) to meet ATP requirements. We’re ensuring the Ohio Department of Veterans Affairs is DSCSA-compliant. And we’ll soon be announcing another exciting initiative in the move toward full serialization of the U.S. pharma supply chain. Keep an eye out for that.
This year, we hosted a “Plan for DSCSA Readiness” webinar in March and a DSCSA 2023 webinar series in June that covered ATPs, EPCIS, and the VRS. We also published a “Dispensers and DSCSA 2023” white paper in May.
We’ve also been helping pharma companies and public-sector organizations comply with the DSCSA and other pharma regulations around the world. From our Serialization Processing and Compliance Management solutions to the full-scale power of our Traceability System, we ensure compliance no matter your role in the supply chain.
Take another look at our DSCSA timeline. A lot has happened since 2013 — and the pace will only intensify over the next two years. Contact us today if you need to know more. Our supply chain and DSCSA experts are here to help and make sure you’re ready for 2023