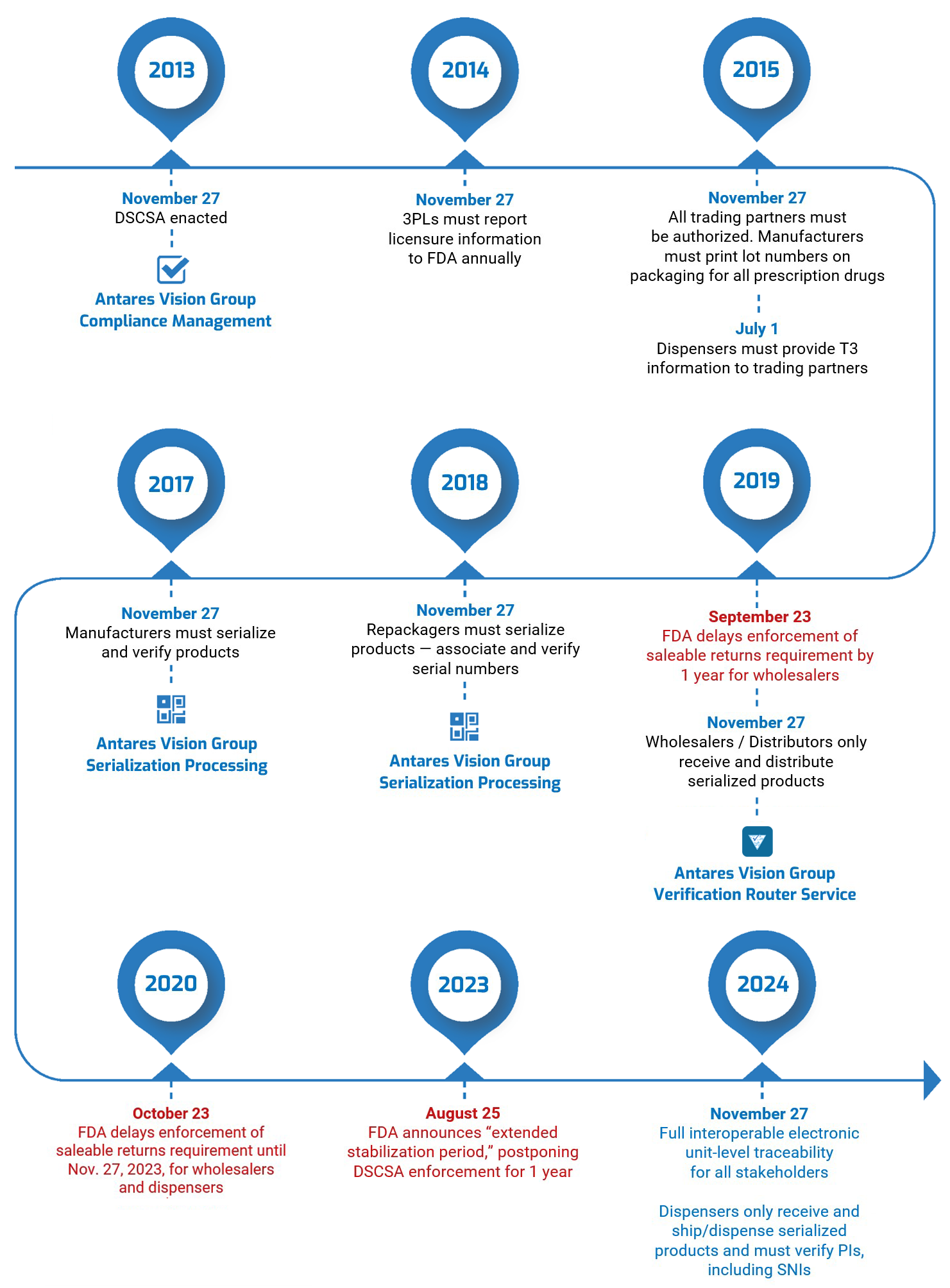
Herb Wong’s a busy guy. We said that the last time we did a DSCSA compliance update with him, and it’s still true today Just last week, for instance, he participated in two Healthcare Distribution Alliance (HDA) webinars, “DSCSA 2023: How a Service Provider Can Help You Prepare” and “All About the VRS.” These were part of the HDA’s 2022 Traceability Webinar Series, which Antares Vision Group is sponsoring.
That’s why it was such a treat to get some one-on-one time with Herb for a real-time DSCSA compliance update — what’s happening right now with industry readiness.
We asked Herb to talk about what he calls “the four cornerstones” of DSCSA compliance: product identification (EPCIS and serialization), product tracing, authorized trading partners (ATPs), and verification (the Verification Router Service, or VRS). Here’s what he had to say.
DSCSA compliance update #1: product identification (EPCIS and serialization)
All solution providers’ systems are ready to send and receive serialization data in the EPCIS format, but we still need to help the industry get data flowing. To use an analogy, even though the pipes have been laid and connected, we’re just not getting enough water through to test for “leaks” in the system — errors in send/receive processing. Just as important, we need time to “flush the pipes” to ensure that we have “clean water.” By that I mean ensuring that the data is correct.
We’re trying to do everything we can. We’ve actually developed a standard process for onboarding customers and getting data exchanged with other solution partners. We’re going to be piloting this so we can refine the onboarding process. [Herb’s talking about the EPCIS Onboarding Guide Workgroup and its draft “Guide for Accelerated EPCIS Onboarding.”]
What’s the key takeaway, Herb?
The key takeaway is, “Let’s connect, let’s get the serialized data out.” Time is running out. That’s the biggest message. People who think they have time to wait until next year, you really don’t. Because what’s going to happen is similar to what happened when the lot-based laws went live: The people who waited couldn’t find help. All the solution providers were busy; everyone was busy. And everyone who waited was trying to get through the same door to meet the deadline.
So, if you’re a manufacturer, you have to start sending data early. If you’re serializing and not sending data downstream, start now. Don’t wait till the November 2023 deadline. You have to “turn on the switch.” Send your data downstream now.
At this point, we decided to ask Herb about aggregation.
DSCSA doesn’t say anything about aggregation. But wholesalers are asking for aggregation to support their business processes. When you send electronic data, wholesalers need to know what serial numbers are in the cases they just received.
Aggregation is a business requirement for operational efficiency. For example, if you get 10 cases with a hundred items in each case, you don’t want to open the cases and scan every item to see what you received and will ultimately ship. Aggregation makes things faster and more efficient. It’s similar to how VRS had both a legal and a business requirement: The legal requirement mandated a response within 24 hours for saleable returns verification. But given the potential volume of saleable returns, 24 hours was too slow for wholesalers; it would cause the receiving docs to fill up with products pending verification. For this reason, wholesalers mandated a business requirement of sub-second response times.
DSCSA compliance update #2: product tracing
A centralized solution or standard has not been defined for product tracing. A lot of different approaches have been discussed, but there’ve been no specs, no firm requirements, that solution providers can implement at this time.
Right now, we’re supporting the industry’s manual process for product tracing. The HDA, NABP, and PDG have done a really good job of outlining what’s required for tracing. [That’s the Healthcare Distribution Alliance, the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy, and the Partnership for DSCSA Governance.]
They’ve walked through a series of scenarios that can be executed manually and have helped the industry to better understand the complexity and nuances of tracing a product through the system. In parallel to this effort, the PDG is working on a data format to communicate traceability requests and responses. PDG is putting that information into a JSON format to communicate the need. [JSON is the JavaScript Object Notation data interchange format. Its advantages are that it uses human-readable text and is a more compact means of communicating data.]
What’s the key takeaway, Herb?
Pay attention to the traceability scenarios that are coming out of the HDA, NABP, and PDG. They’re doing a really good job of trying to show how tracing workflows will happen. They’ll be publishing more results and helping the industry understand. Watch for these, because it will enlighten you about what’s coming in 2023.
DSCSA compliance update #3 and #4: ATPs and VRS
From a solution provider standpoint, the ATP and VRS initiatives have become one and the same. Right now, ATPs have only been applied against the VRS, so the timing for us to get that done has become one implementation effort.
When you make a VRS request, you have to prove you’re an ATP. ATP is there to confirm two things: you are who you say you are and you are authorized to transact business. Proof that you are an ATP is especially important in the VRS network since trading partners may not have direct relationships with other VRS participants.
For VRS, there’s a new version 1.3 that will be deployed before the DSCSA 2023 deadline. The current version we have is based on the 1.2 standards interface. The 1.3 version “opens up” VRS beyond what it was intended to do, which is the verification of saleable returns.
What people should know is that VRS 1.3 is not backwards-compatible. This means VRS providers have to upgrade at once. To ensure that the upgrade occurs on time, solution providers have agreed to “decouple” the 1.3 interface from the 1.3 functionality.
What this means is that everyone on the VRS network will remain connected since we will all support the new 1.3 connections. However, solution providers (or customers) who are not ready to upgrade to the new 1.3 functionality can continue to use VRS as needed. That’s going to be important because it allows us to change the interface so we can at least keep talking to each other. We can be interoperable. But not everyone has to support the features of 1.3 at the same time.
As for timing of the update, we’re talking about doing the testing of the interoperability of 1.3 in Q1 [of 2023]. So we’ll have to push this into a production environment after Q1, but we haven’t agreed on a production date.
What’s the key takeaway, Herb?
There is going to be an upgrade required soon and the industry and solution providers are working to make sure it’s easy to implement. We realize that is not as simple as a software upgrade but we need to carefully consider the revalidation requirements of our customers.
Final thoughts
And there you have it: A DSCSA compliance update about what’s happening right now with industry readiness for product identification (EPCIS and serialization), product tracing, and ATPs and VRS. Thanks, Herb!
Contact us if you have questions about what Herb talked about or the DSCSA in general. We can explain the requirements and how our solutions will help ensure you’re ready for November 2023 and the full serialization of the U.S. pharmaceutical supply chain.
If you like, we can probably arrange a meeting with Herb. But remember, he’s busy. In the coming weeks, he’ll travel to the Antares Vision Group global HQ in Italy, visit the Group’s brand-new North America HQ in New Jersey, and join a panel discussion at the HDA Traceability Seminar in Washington, D.C. (Antares Vision Group is also a sponsor of that annual event.) So reach out today and let’s see what we can work out.
Also take a look at our DSCSA Compliance Library. It’s a clearinghouse of information with links to our blog posts, white papers, webinars — everything — about the law, including the “four cornerstones” Herb talked about in today’s DSCSA compliance update.