The Drug Quality and Security Act (DQSA) was enacted on November 27, 2013, to address gaps and oversights in the way compound medications — medications that are customized by combining, mixing, or altering two or more drugs to meet the needs of a specific patient — are prepared and distributed. It was a response to the inadvertent distribution of contaminated steroidal injections that killed 64 people and caused infections in 793 patients.
The DQSA comprises two pieces of legislation: The Compounding Quality Act and the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA). Here’s a quick overview of each.
DQSA Part 1: The Compounding Quality Act
The goal of the Compounding Quality Act is to make compounded medicines safer for patients. It established a registration system for pharmaceutical industry stakeholders that create sterile drugs (e.g., manufacturers and pharmacies). It also reinstated Section 503A of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act), parts of which the Supreme Court in 2002 ruled unconstitutional.
Companies can register as an official outsourcing facility if they meet a specific set of criteria. Outsourcing facilities are usually larger companies that supply compounds to healthcare facilities such as pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics. The key requirements for outsourcing facilities under the Compounding Quality Act include the following:
- They must report adverse events to the FDA twice a year.
- They must submit reports about all compounded medications to the FDA twice a year
- They must meet product labeling requirements.
- They must agree to FDA inspections (according to a “risk-based schedule” and pay fees for any re-inspections.
- They must pay a registration fee to the FDA.
Outsourcing facilities are also subject to increased quality standards and can be penalized for certain actions, including intentionally falsifying prescriptions for compounded medicines, failing to report adverse events or compounded medications to the FDA, making false claims about compounded medicines (i.e., false advertising), and selling medications with “not for resale” warnings.
All this said, it’s important to note that the FDA does not approve compounded drugs. The Agency does not verify their safety or effectiveness. Furthermore, compounded drugs do not have an FDA finding of manufacturing quality before they are marketed.
DQSA Part 2: The Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA)
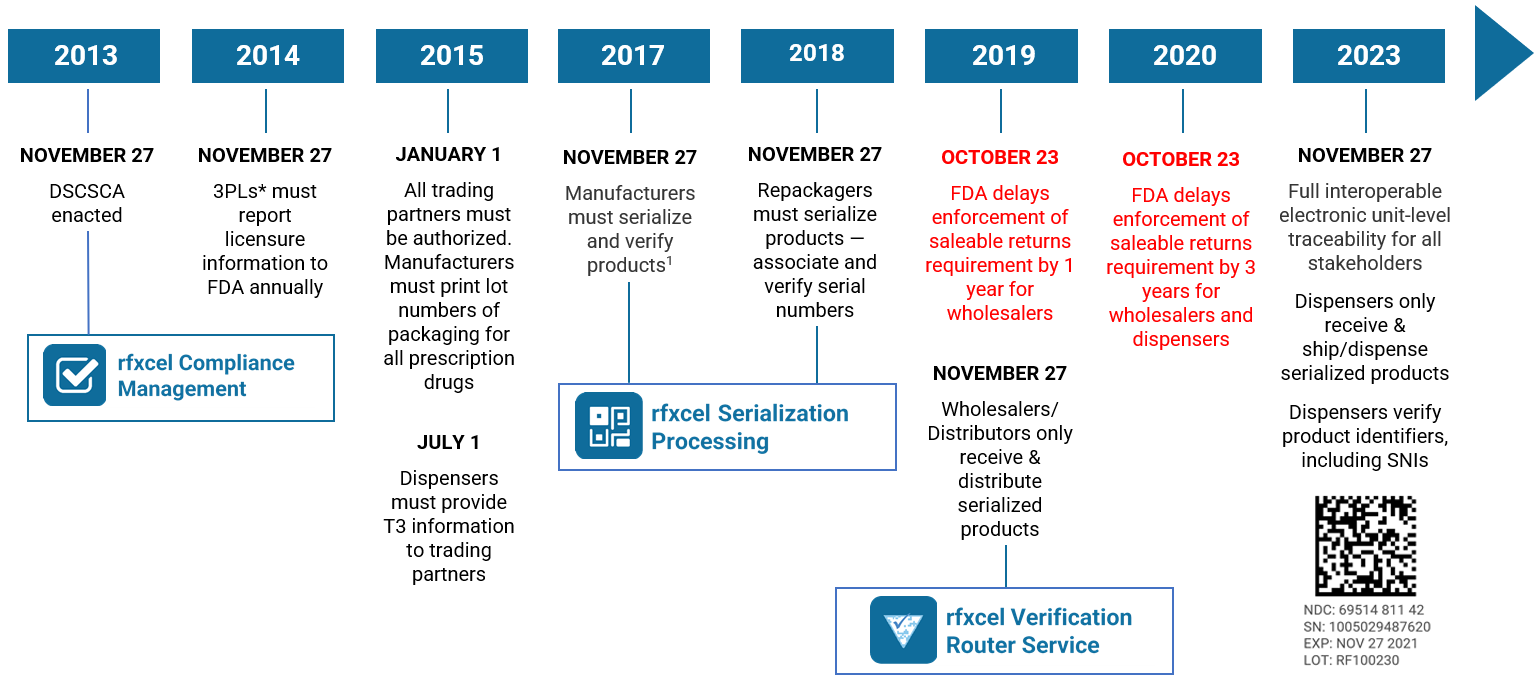
The DSCSA is a wide-ranging piece of legislation designed to prevent counterfeit, stolen, contaminated, or otherwise harmful drugs from entering the U.S. pharmaceutical supply chain. It affects virtually every industry stakeholder, from manufacturers, distributors, and wholesalers to repackagers, logistics providers, and dispensers (i.e., pharmacies). It is
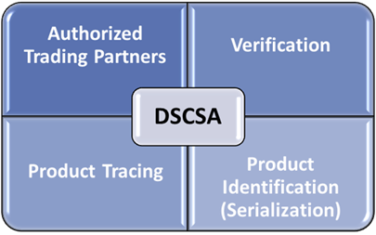
Enacted in November 2013 and culminating with the November 2023 deadline, the ultimate goal of the DSCSA is a fully serialized pharmaceutical supply chain with full electronic operability. There are four core requirements:
- Product serialization
- Product tracing
- Verification (of product identifiers)
- Authorized trading partners
If you follow our blog, you know we’ve been writing about the DSCSA for years. For a longer summary, check out “Countdown to DSCSA 2023 Serialization: The Deadline Is Two Years Away.” For an in-depth look at what’s in store for 2023, read “DSCSA 2023: The Future of Pharmaceutical Traceability in the USA.”
Final thoughts
rfxcel has been the leading provider of regulatory and compliance software for the pharmaceutical industry for almost 20 years. We’ve also been a thought leader on the DQSA and DSCSA compliance. Our goal is to keep all stakeholders informed and work with them to ensure they’re ready to meet all the requirements in 2023.
Below are a few of our most recent resources to help bring you up to speed. Take a look, and if you have any questions or want to see a short demo of our DQSA and DSCSA solutions, contact us today. Our supply chain experts know the legislation inside and out and will work with you to design a solution that’s right for you.