Just a little over four months into the FDA’s DSCSA extended stabilization period and with the clock ticking down to the November 27, 2024, compliance deadline, EPCIS DSCSA exceptions handling is top-of-mind in the pharma industry.
But why? Let’s take a look at EPCIS DSCSA exceptions handling and how we can deal with it to ensure DSCSA compliance.
EPCIS DSCSA Exceptions Handling Keeps Your Products Flowing
The DSCSA requires the interoperable, electronic exchange of serialized product data. Specifically, trading partners must exchange Transaction Information (TI) and Transaction Statement (TS) data every time a regulated drug changes hands.
Exceptions are errors that may occur when partners exchange this data using EPCIS. If there’s an exception, the product cannot move forward in the supply chain, which means it won’t reach patients and consumers in a timely manner. Furthermore, if exceptions aren’t resolved quickly, a product could be considered suspect or illegitimate.
This is why EPCIS DSCSA exceptions handling is top-of-mind for the pharmaceutical industry.
Given the complex nature of securely exchanging serialized product data, it’s logical to expect exceptions, especially in the early days of enforcement. The Healthcare Distribution Alliance (HDA) has identified six categories of EPCIS DSCSA exceptions:
- Data Issues
- Damaged Products
- Product, No Data
- Data, No Product
- Packaging
- Product Hold
Exceptions have been on the HDA’s radar for years. At its Traceability Online Seminar in November 2021, for example, industry leaders discussed establishing standards for dealing with exceptions. They also discussed example scenarios, such as overages as a “Product, No Data” exception. In this scenario, a downstream trading partner might have 16 cases arrive at its facility but receive EPCIS data for only 15 of those cases. How does it notify the manufacturer? How does the manufacturer correct the TI so the case can be removed from quarantine and be on its way?
The message is clear: Trading partners must focus on building a system that quickly communicates and resolves data issues so products can keep moving.
Note: Also remember that the DSCSA requires all partners to be authorized trading partners (ATPs). This isn’t necessarily relevant to our discussion today, but it’s a critical part of compliance.
EPCIS DSCSA Exceptions Handling Solutions: Communication and Collaboration
The most important thing to remember about dealing with exceptions is that trading partners must communicate and collaborate. You are not working in a vacuum, and there is not a “lone wolf” solution for exceptions handling.
Herein lies the challenge. The communication infrastructure in the pharma supply chain — emails, online portals, phone calls, and so on — wasn’t designed with DSCSA compliance in mind, let alone dealing with exceptions handling in an interoperable, electronic data-exchange system.
So, in order for an EPCIS DSCSA exceptions handling solution to be effective, it must be built on a foundation of fast, targeted, and precise communication between/among the right people. In the overages example above, this would mean the trading partner that received the extra case would know exactly who to contact at the manufacturer, what information to share with that person, and how long it would take to fix the data error.
Are You Ready for EPCIS DSCSA Exceptions Handling?
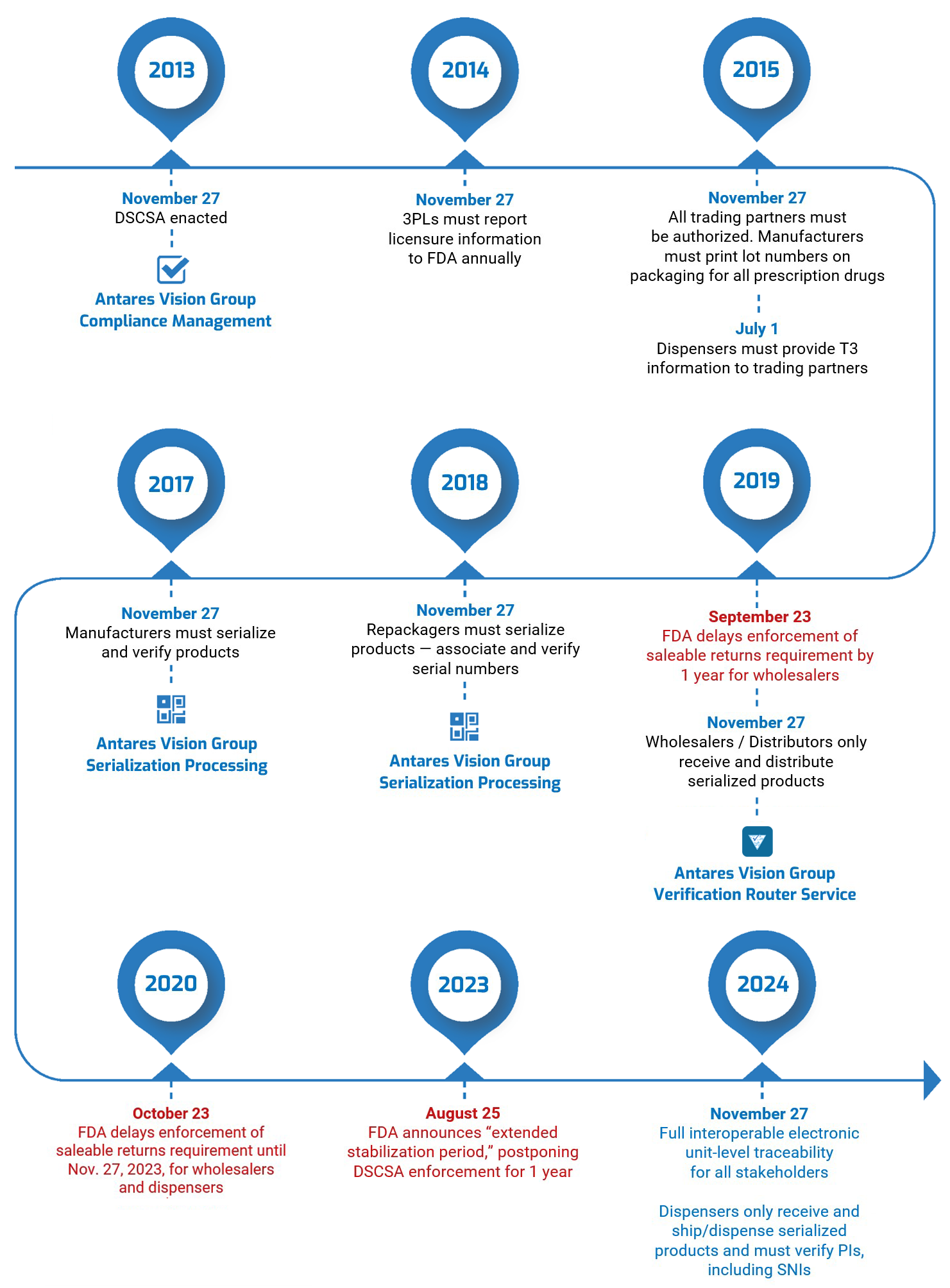
The FDA’s extended stabilization period has given the pharmaceutical industry an additional year to prepare for the full serialization of the U.S. drug supply chain, including being able to deal with EPCIS DSCSA exceptions handling.
This is good news for everyone. But you have to use this time to ask yourself the tough questions:
- Do you have systems up and running?
- Are you testing your systems?
- Are you communicating and collaborating with all of your trading partners?
- Are you complying with the DSCSA requirements that are enforceable right now?
- Are you working with a solution provider that fully understands your role in the supply chain, your product(s), your business, and your DSCSA compliance needs?
- Are you going to be ready for November 27, 2024?
We are here to help. We have led on the DSCSA since rollout began in 2014. Today, we’re working with the industry to develop a collaborative approach to exceptions handling using GS1-based error correction.
Don’t let bad data disrupt your business. Contact us today to learn more. We’ll ensure you receive compliant data from your trading partners, quickly resolve data quality issues, and keep your products moving.